-->
Nov 30, 2019 Mac OS X and macOS have a few restrictions in place about which items you can remove. The Finder and the Trash are permanent members of the Dock. There's also a separator (a vertical line or dotted line icon) that marks where apps end and documents, folders, and other items begin in the Dock. Oct 11, 2019 Your Mac will take a while to gather information about your apps and then displays a list of all the apps on your machine. Find the column headed '64-bit (Intel)' and click on the column heading.
The Docker Engine and client aren't included with Windows and need to be installed and configured individually. Furthermore, the Docker Engine can accept many custom configurations. Some examples include configuring how the daemon accepts incoming requests, default networking options, and debug/log settings. On Windows, these configurations can be specified in a configuration file or by using Windows Service control manager. This document details how to install and configure the Docker Engine, and also provides some examples of commonly used configurations.
Install Docker
You need Docker in order to work with Windows Containers. Docker consists of the Docker Engine (dockerd.exe), and the Docker client (docker.exe). The easiest way to get everything installed is in the quickstart guide, which will help you get everything set up and run your first container.
For scripted installations, see Use a script to install Docker EE.
Before you can use Docker, you'll need to install the container images. For more information, see docs for our container base images.
Docker Android App
Configure Docker with a configuration file
Disable Apps Stay Docker Mac Os
The preferred method for configuring the Docker Engine on Windows is using a configuration file. The configuration file can be found at 'C:ProgramDataDockerconfigdaemon.json'. You can create this file if it doesn't already exist.
Note
Not every available Docker configuration option applies to Docker on Windows. The following example shows the configuration options that do apply. For more information about Docker Engine configuration, see Docker daemon configuration file.
You only need to add the desired configuration changes to the configuration file. For example, the following sample configures the Docker Engine to accept incoming connections on port 2375. All other configuration options will use default values.
Likewise, the following sample configures the Docker daemon to keep images and containers in an alternate path. If not specified, thedefault is c:programdatadocker.
The following sample configures the Docker daemon to only accept secured connections over port 2376.
Configure Docker on the Docker service
The Docker Engine can also be configured by modifying the Docker service with sc config. Using this method, Docker Engine flags are set directly on the Docker service. Run the following command in a command prompt (cmd.exe not PowerShell):
Note
You don't need to run this command if your daemon.json file already contains the 'hosts': ['tcp://0.0.0.0:2375'] entry.
Common configuration
The following configuration file examples show common Docker configurations. These can be combined into a single configuration file.
Default network creation
To configure the Docker Engine so that it doesn't create a default NAT network, use the following configuration.
For more information, see Manage Docker Networks.
Set Docker security group
When you've signed in to the Docker host and are locally running Docker commands, these commands are run through a named pipe. By default, only members of the Administrators group can access the Docker Engine through the named pipe. To specify a security group that has this access, use the group flag.
Proxy configuration
To set proxy information for docker search and docker pull, create a Windows environment variable with the name HTTP_PROXY or HTTPS_PROXY, and a value of the proxy information. This can be completed with PowerShell using a command similar to this:
Once the variable has been set, restart the Docker service.
For more information, see Windows Configuration File on Docker.com.
How to uninstall Docker
This section will tell you how to uninstall Docker and perform a full cleanup of Docker system components from your Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 system.
Note
You must run all commands in these instructions from an elevated PowerShell session.
Prepare your system for Docker's removal
Before you uninstall Docker, make sure no containers are running on your system.
Run the following cmdlets to check for running containers:
It's also good practice to remove all containers, container images, networks, and volumes from your system before removing Docker. You can do this by running the following cmdlet:
Uninstall Docker
Next, you'll need to actually uninstall Docker.
To uninstall Docker on Windows 10
- Go to Settings > Apps on your Windows 10 machine
- Under Apps & Features, find Docker for Windows
- Go to Docker for Windows > Uninstall
To uninstall Docker on Windows Server 2016:
From an elevated PowerShell session, use the Uninstall-Package and Uninstall-Module cmdlets to remove the Docker module and its corresponding Package Management Provider from your system, as shown in the following example:
Tip
You can find the Package Provider that you used to install Docker with PS C:> Get-PackageProvider -Name *Docker*
Clean up Docker data and system components
After you uninstall Docker, you'll need to remove Docker's default networks so their configuration won't remain on your system after Docker is gone. You can do this by running the following cmdlet:
To remove Docker's default networks on Windows Server 2016.
Run the following cmdlet to remove Docker's program data from your system:
You may also want to remove the Windows optional features associated with Docker/containers on Windows.
This includes the 'Containers' feature, which is automatically enabled on any Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 when Docker is installed. It may also include the 'Hyper-V' feature, which is automatically enabled on Windows 10 when Docker is installed, but must be explicitly enabled on Windows Server 2016.
Important
The Hyper-V feature is a general virtualization feature that enables much more than just containers. Before disabling the Hyper-V feature, make sure there are no other virtualized components on your system that require Hyper-V.
To remove Windows features on Windows 10:
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features > Turn Windows features on or off.
- Find the name of the feature or features you want to disable—in this case, Containers and (optionally) Hyper-V.
- Uncheck the box next to the name of the feature you want to disable.
- Select 'OK'
To remove Windows features on Windows Server 2016:
From an elevated PowerShell session, run the following cmdlets to disable the Containers and (optionally) Hyper-V features from your system:
Reboot your system
To finish uninstallation and cleanup, run the following cmdlet from an elevated PowerShell session to reboot your system:
Your Mac comes with a small panel along the edge of the screen called the Dock: It lets you quickly access your favorite apps, files, and folders, as well as any actively-running apps. When you save an item to the Dock, you can access it at any time by clicking on it.
By default, most of Apple's built-in apps start with shortcuts saved in the Dock, but you can also remove those shortcuts and add your own. You can also customize the Dock to fit your preferences. Here's how.
What is the Dock, and what gets displayed there?
The Dock has been with the Mac for over a decade, now: It offers you a quick way to access the Finder (your Mac's underlying filesystem) as well as your currently running applications, favorite apps, favorite files or folders, and the Trash.
When you first set up your Mac, your Dock lives along the bottom of your screen in a translucent rectangle; if you don't like its positioning, you can move it to the left or right of the screen, or have it automatically hide whenever you're not interacting with it. Items are organized as follows, left to right:
- The Finder
- Favorite app shortcuts
- Currently-running apps (you can also choose in the Dock preferences whether you want to view an indicator (a little black dot) for currently-open apps)
- Favorite files or folders
- The Trash
Though you can shuffle the position of app shortcuts in the Dock, you can't move the Finder or Trash — they live on opposite ends of the Dock, respectively — nor can you mix file shortcuts with apps in the same section.
How to add apps to the Dock on your Mac
- Launch a Finder window from your Dock.
Click on Applications in the sidebar.
- Select an app and drag it to the Dock.
Let go of the app while it hovers over the Dock.
If you want to permanently add a currently-running app to your Dock:
- Right-click or Control-click on the app icon in the Dock.
- Select Options under the drop-down menu.
- Click on Keep in Dock.
You can alternatively just drag the icon to a different position in your Dock, which will automatically save it as a favorite shortcut.
How to add files and folders to the Dock on your Mac
Files and folders can also be saved to your Dock, but they can only be stored on the far right of the Dock, after your app shortcuts. The Dock has a demarcating line that separates apps from files and folders, so you won't mix them up.
- Launch a Finder window from your Dock.
- Select a file or folder from its location on your Mac and drag it to the right side of the Dock.
- Let go of the file or folder while it hovers over the right side of the Dock.
How to remove apps, files, and folders from the Dock on your Mac
If you don't want a particular app, file or folder in your Dock anymore, you can remove it with just one gesture. Note that this doesn't remove the item from your computer, it just removes the shortcut from the Dock; you can always re-add the app or folder by following the steps above.
Select an app, file, or folder and drag it out of the Dock.
When it is hovering over your desktop, you will see the word Remove appear above the app, file, or folder.
Let go of the app, file, or folder. It will disappear from the Dock.
Repeat the steps above to remove all items you no longer want to kept in the Dock.
Note: If you do this on a currently-open app, it will continue to stay in the Dock until you Quit the application, at which point it will disappear.
How to organize the Dock on your Mac
You can rearrange the placement of apps, files, and folders in your Dock so they are in alphabetical order, color-coordinated, or however you like.
Note: You can't move the Finder or Trash icons to the far left and right of the Dock respectively. They are anchored to the Dock because of their importance to the system.
- Select an app, file, or folder in the Dock.
- Drag it to a new location in the Dock.
Let go of the app, file, or folder while it hovers over the new location in the Dock.
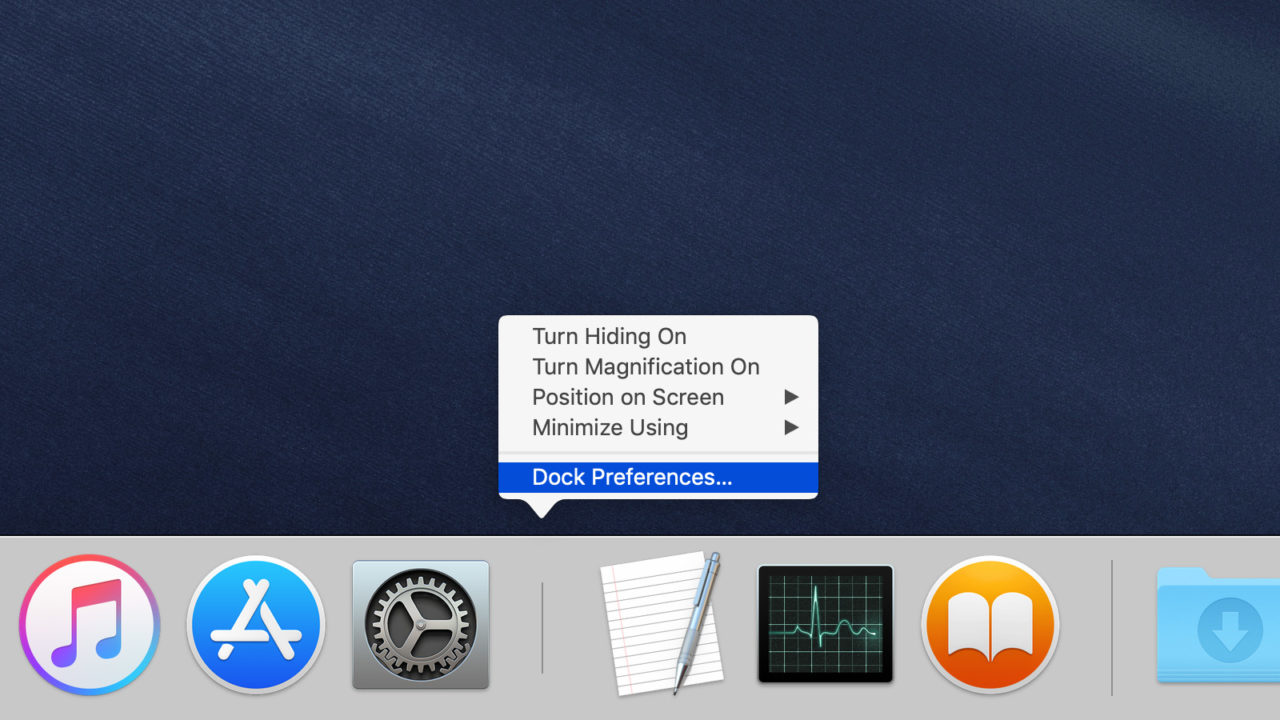
How to change the Dock's size on your Mac
You can adjust the size of the dock so that icons are larger or smaller on your screen.
- Click on the Apple icon in the upper left corner of your Mac's screen.
Select System Preferences from the drop down menu.
- Click on Dock.
Drag the Size slider to the left or right to increase or decrease the size of the Dock.
- Tick the box for Magnification to enable an animation that makes the items in the Dock that your cursor hovers over larger.
Drag the Magnification slider to the left or right to increase or decrease how large the icons grow when your cursor hovers over them.
How to change the Dock's orientation on your Mac
You can display the Dock on the bottom, right, or left side of your screen.
- Click on the Apple icon in the upper left corner of your Mac's screen.
Select System Preferences from the drop down menu.
- Click on Dock.
Select Left, Bottom, or Right to change the orientation of the Dock.
How to automatically hide or show the Dock on your Mac
On smaller laptop screens, every bit of screen space is valuable. If you don't want the Dock getting in the way of your productivity, you can keep it hidden until you want to access it, at which point, you can call it back up by hovering your cursor over the place where it normally resides.
- Click on the Apple icon in the upper left corner of your Mac's screen.
Select System Preferences from the drop down menu.
- Click on Dock.
Tick the box for Automatically hide and show the Dock.
How to hide recent applications on the Dock on macOS Mojave
Much like iOS on the iPad, macOS Mojave puts users' recently-used applications in a special section of the Dock. If this doesn't sound like your cup of tea, it's easy enough to turn off.
- Open System Preferences from your Dock or Applications folder.
Click Dock.
Click the checkbox next to Show recent applications in Dock so that the check disappears (it's on by default).
You can check the box if you decide you want to use this feature.
Bonus: Pro tips for using the Dock
You can change the size of the Dock by positioning the cursor over the Dock divider that separates apps from files and folders. The cursor will change to a double-sided arrow; click and drag to increase or decrease the size of the Dock.
You can change the location of the Dock by holding down the shift key, clicking on that divider, and dragging the Dock to the left, bottom, or right sides of the screen.
If you'd like to keep an app that's open in the Dock permanently, right or control-click the icon in the Dock, select Options and select Keep in Dock.
If you want to add spacers between apps, there's a Terminal command to do so.
macOS Catalina
Main
We may earn a commission for purchases using our links. Learn more.
My heartThis timelapse of macOS 10.0 through 10.15 is a nostalgic wonder
The very first version of macOS, or Mac OS X as it was known, arrived almost 20 years ago. This video takes us through every major update the Mac has seen since in one amazing timelapse.